The Importance of Biotin for Healthy Hair
What is Biotin?
Biotin is a water-soluble vitamin B that is vital for human health. It is also known as Vitamin H or B7 and is essential for a variety of metabolic processes in the body, such as the synthesis of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids. Biotin also aids in the conversion of food into energy, the synthesis of hormones, and the maintenance of healthy skin, hair, and nails. It can be found in a range of foods, including egg yolks, liver, yeast, and whole grain cereals, as well as in dietary supplements.
The Importance of Biotin for Hair Health
While we all know biotin as vitamin B7, it is also known as "Vitamin H," where "H" stands for "Haar" and "Haut," which are German words for "skin" and "hair," respectively. Biotin plays an important role in stimulating keratin production in your hair to boost follicle growth and strengthen it from within, thereby reducing hair fall and supporting the growth of your hair follicles. It further strengthens your hair by reducing breakage.
Using a variety of shampoos, conditioners, or masks with several chemicals may not help your hair as much as ingesting vitamins and minerals. "You are what you eat" and so is your hair. With the rising intake of fast food and processed foods, the body loses out on these essential nutrients. Hence, it is necessary to consume foods that are rich in elements that are essential for your hair growth and overall well-being. Needless to say, biotin is one of these nutrients that should be a must in your diet.
What is Pure Biotin Vitamin b7 Uses?
Biotin helps support healthy hair, skin, nails, and metabolic function. Biotin also converts proteins, carbohydrates, and fats into useable energy within the body. Vitamin B7 helps the body use glucose for energy as well. Biotin activates acetyl-coA carboxylase, an enzyme that helps synthesize myelin. Myelin acts as an insulating layer of ‘sheath’ that protects nerves.
Biotin for Hair
Keratin proteins are the primary components of hair, skin, and nails. Biotin supports keratin’s foundation, and it may provide hair health benefits. One study found that biotin supplements reduced hair shedding and improved hair growth in thinning areas. Another study supported these findings and noted improved hair quality.
Biotin for Skin
Biotin deficiency can cause skin problems, including red and scaly skin. Biotin crosses the skin barrier with ease and can increase serum levels of B7 from topical applications. Biotin may help hydrate and smooth skin for an overall better appearance.
Biotin for Nails
Biotin may convey significant benefits for nail health and appearance. One study found that biotin supplements reduced nail splitting and improved nail thickness, particularly in participants with brittle nails.
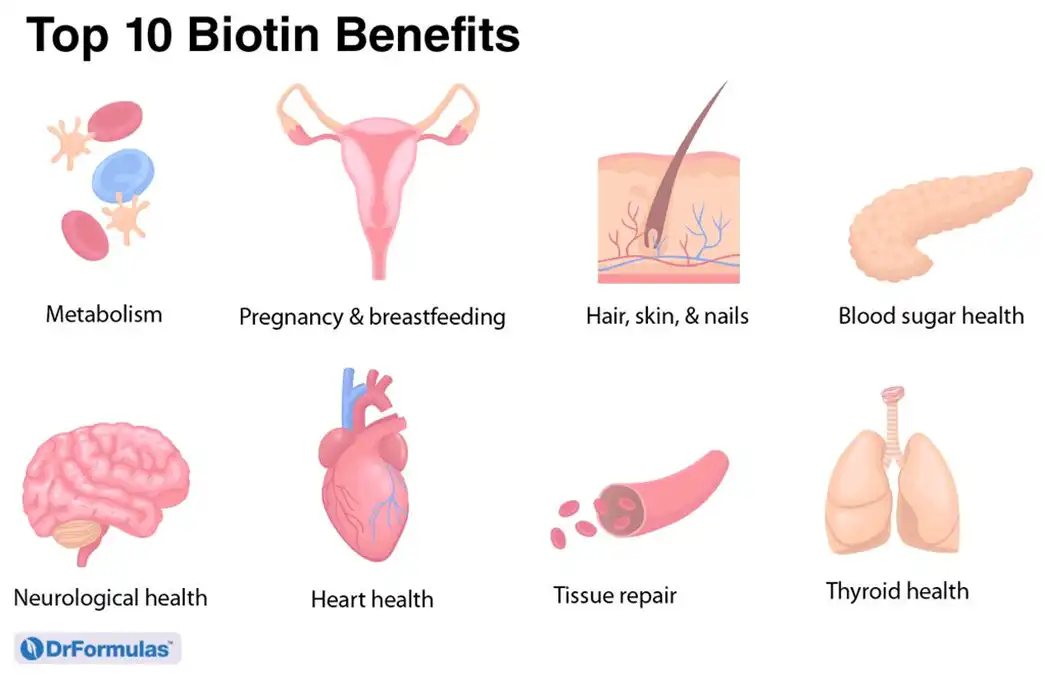
Health Benefits of Biotin
Biotin, offers numerous health advantages, including the following:
- · Biotin for skin and hair: It is essential for the health of the skin, hair, and nails, and a shortage of biotin can result in hair loss, brittle nails, and skin rashes.
- · Maintains healthy blood sugar levels: Biotin has been demonstrated to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetics.
- · Promotes nerve health: Biotin is important in the generation of nerve transmitters, and a lack of biotin has been related to nerve injury and peripheral neuropathy.
- · Biotin in pregnancy and lactation: It is essential for fetal growth, and a biotin shortage during pregnancy has been related to an increased risk of birth abnormalities.
- · Boosts energy levels: Biotin aids in the conversion of food into energy and is involved in the metabolism of lipids and carbohydrates, all of which can contribute to increased energy levels.
- · Increases enzyme efficiency: Biotin aids in utilizing enzymes and carrying nutrients throughout the body.
- · Eye Health: It helps prevent macular degeneration (vision impairment).
- · Detoxification: Biotin aids in the detoxification and improvement of liver function, particularly in those with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver cirrhosis.
Pure Biotin and the Environment
- Sustainable Sourcing: Biotin is often derived from natural sources, such as yeast and certain bacteria, which can be produced through environmentally friendly fermentation processes.
- Minimal Environmental Impact: The production of biotin typically requires fewer resources and less energy compared to synthetic vitamins, resulting in a lower carbon footprint.
- Biodegradable: Pure biotin is a natural compound that is biodegradable, reducing environmental pollution associated with synthetic alternatives.
- Supports Plant-Based Diets: As a supplement often used in plant-based diets, biotin contributes to sustainable living by promoting vegan and vegetarian lifestyles.
- Recycling Nutrients: Biotin aids in metabolic processes that help plants and animals efficiently use nutrients, supporting overall ecosystem health.
- Reduced Chemical Use: Natural biotin production minimizes the need for harmful chemicals and additives, leading to less environmental contamination.
- Encourages Sustainable Practices: The demand for biotin from natural sources promotes agricultural practices that are more sustainable and ecologically responsible.
How long does it take for biotin to work?
It may take a few months or longer for increased levels of biotin in your body to pay off. You will need to be patient and committed.
An easy way to maximize this vitamin in your body is by improving your diet and concentrating on foods rich in biotin.
Nuts, seeds, legumes, and leafy greens are some excellent examples.
It’s important to note that increased biotin in your system does not automatically mean your hair loss will stop – it will only have an impact if you’re currently suffering from a deficiency.
The best foods to increase your biotin intake
For average nutritional values, take a look at the best sources of biotin infographic below:
|
Food item |
Biotin content |
Daily value |
|
Egg yolk (50 grams) |
10 mcg |
33% |
|
Mushroom (70 grams) |
5.6 mcg |
19% |
|
Chicken liver (75 grams) |
138 mcg |
460% |
|
Salmon (85 grams) |
5 mcg |
17% |
|
Banana (105 grams) |
0.2 mcg |
1% |
|
Avocado (200 grams) |
1.85 mcg |
6% |
|
Sweet potatoes (125 grams) |
2.4 mcg |
8% |
|
Pork chop (85 grams) |
3.8 mcg |
13% |
|
Spinach (64 grams) |
5 mcg |
17% |
The benefits of biotin for hair
Biotin is the hair supplement that ticks all the boxes: Growth? Check! ✓ Reinforcement? Check! ✓ Thickening? Check too! ✓
1) Hair Growth
Biotin stimulates cell division in hair follicles (tiny structures located under the skin from which hair grows), thereby promoting hair growth . In addition, it prolongs the growth phase of the hair cycle, which reduces hair loss.
2) Strengthening and thickening
Through its role in the production of keratin, biotin helps strengthen hair structure, making it less prone to breakage. Additionally, it can help increase hair diameter, perfect for making hair look thicker and fuller.
3) Improved scalp quality
Adequate consumption of biotin can also promote a healthy scalp by reducing irritation and inflammation. And a healthy scalp is essential for strong, vigorous hair.
Pure Biotin Nutrition Facts
Pure Biotin Nutrition Facts (per serving with 30 mcg)
- Calories: 0
- Total Fat: 0 g
- Sodium: 0 mg
- Total Carbohydrates: 0 g
- Dietary Fiber: 0 g
- Sugars: 0 g
- Protein: 0 g
- Biotin: 30 mcg (100% DV*)
*DV = Daily Value based on a 2,000-calorie diet.
Additional Nutrients (if included in a supplement):
Vitamin B Complex: May contain other B vitamins for synergistic effects.
Wrapping up, Pure Biotin is a very important ingredient for your health especially for your hair, nail and skin health. While there are multiple food sources of biotin people need to take biotin supplements in case of biotin deficiency to address any health issue. Biotin supplements are effective for hair loss and skin issues caused by a biotin deficiency. While choosing any biotin supplement make sure you are choosing natural biotin supplements and not synthetically sourced biotin supplements.
Where to Buy Pure Biotin Powder?
You can purchase Pure Biotin powder available with free sample at yanggebiotech.com. The company is an industry-leading manufacturer and distributor for pure dietary supplements. YANGGE BIOTECH INGREDIENTS is not just a consumer brand. It also supplies pure ingredients to other brands that distribute food and other supplement products. Contact Us to place an order today.
References:
● DiMarco G, McMichael A. Hair Loss Myths. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017 Jul 1;16(7):690-694. PMID: 28697221, (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28697221/)
● Said HM. Biotin: biochemical, physiological and clinical aspects. Subcell Biochem. 2012;56:1-19. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-2199-9_1. PMID: 22116691. (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22116691/)
● Patel DP, Swink SM, Castelo-Soccio L. A Review of the Use of Biotin for Hair Loss. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017;3(3):166-169. doi:10.1159/000462981. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5582478/)
● Lipner SR. Rethinking biotin therapy for hair, nail, and skin disorders. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jun;78(6):1236-1238. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.02.018. Epub 2018 Feb 10. PMID: 29438761. (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29438761/)
● Biotin, National Institute of Health, (https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Biotin-HealthProfessional/)
● Hemmati M, Babaei H, Abdolsalehei M. Survey of the effect of biotin on glycemic control and plasma lipid concentrations in type 1 diabetic patients in kermanshah in iran (2008-2009). Oman Med J. 2013;28(3):195-198. doi:10.5001/omj.2013.53. ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3679599/)
● Abramson DH, Abramson HS. High-Dose Supplements for Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Did You Leave Out Centrum? Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120(11):1602. (https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaophthalmology/article-abstract/272777)
● Zempleni J, Wijeratne SS, Hassan YI. Biotin. Biofactors. 2009;35(1):36-46. doi:10.1002/biof.8. (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4757853/#)
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Unlocking the Benefits of NMN Powder for Longevity
- Amylase Enzyme Function
- trans resveratrol para que serve benefits for skin
- Algae Omega 3 Supplement Benefits
- Organic Turmeric Root Powder Natural Benefits
- Ultimate Micronized Creatine Monohydrate Powder
- how does tongkat ali increase testosterone?
- What is oat beta-glucan used for?
- Does instant white tea have any health benefits?
- 5 Easy Butterfly Pea Tea Drinks To Make | Cafe Drink Ideas