Top Benefits of Eicosapentaenoic Acid
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is a remarkable omega-3 fatty acid that offers numerous health benefits. Found primarily in fatty fish and fish oil supplements, EPA has garnered significant attention in the health and wellness community. This essential nutrient plays a crucial role in supporting heart health, reducing inflammation, and promoting optimal brain function. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the top benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid and why incorporating it into your diet could be a game-changer for your overall well-being.

How Eicosapentaenoic Acid Supports Heart Health?
EPA has emerged as a potent ally in the quest for cardiovascular wellness. Its impact on heart health is multifaceted, addressing several key factors that contribute to cardiovascular disease risk.
1. Lowering Triglyceride Levels: One of the most notable benefits of EPA is its ability to reduce triglyceride levels in the bloodstream. Elevated triglycerides are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. EPA works by inhibiting the liver's production of triglycerides and enhancing their clearance from the bloodstream. This dual action helps maintain healthier lipid profiles, potentially reducing the risk of cardiovascular events.
2. Improving Cholesterol Balance: While EPA may not significantly lower total cholesterol, it has a positive impact on cholesterol balance. It helps increase levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, often referred to as "good" cholesterol, which plays a crucial role in removing excess cholesterol from the bloodstream. By promoting a more favorable ratio of HDL to LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, EPA contributes to better cardiovascular health.
3. Reducing Blood Pressure; Hypertension is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Vagen EPA has been shown to have a modest but beneficial effect on blood pressure. It helps relax blood vessels, improving their elasticity and reducing resistance to blood flow. This vasodilatory effect can lead to lower blood pressure readings, particularly in individuals with mild hypertension.
4. Preventing Arterial Plaque Formation: EPA possesses anti-atherogenic properties, meaning it helps prevent the formation of plaque in the arteries. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the arterial walls, EPA can slow down the progression of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries. This protective effect is crucial for maintaining healthy blood flow and reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.

The Role of EPA in Reducing Inflammation
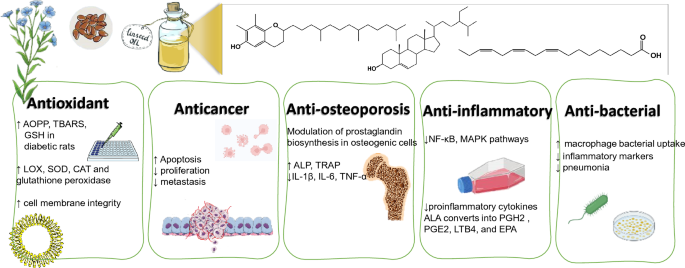
Inflammation is a double-edged sword in the body. While acute inflammation is a necessary part of the immune response, chronic inflammation can lead to a host of health problems. EPA plays a significant role in modulating the inflammatory response, offering potential benefits for various inflammatory conditions.
1. Producing Anti-Inflammatory Mediators: Vagen EPA serves as a precursor to a group of molecules called resolvins and protectins. These specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) are potent anti-inflammatory compounds that help resolve inflammation and promote tissue healing. By increasing the production of these beneficial molecules, EPA helps to keep inflammation in check and prevent it from becoming chronic.
2. Balancing Omega-6 to Omega-3 Ratio: The modern Western diet is often characterized by an imbalance between omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids, with an excess of omega-6. This imbalance can promote inflammation. EPA helps restore a healthier balance by increasing omega-3 levels in the body. A more balanced ratio of these essential fatty acids can lead to a reduction in overall inflammation and associated health risks.
3. Alleviating Joint Pain and Stiffness: For individuals suffering from inflammatory joint conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, EPA offers potential relief. Its anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. While not a replacement for conventional treatments, EPA supplementation may serve as a complementary approach to managing inflammatory joint disorders.
4. Supporting Skin Health; EPA's anti-inflammatory effects extend to the skin, potentially benefiting those with inflammatory skin conditions like psoriasis and eczema. By reducing inflammation and supporting the skin's barrier function, EPA may help alleviate symptoms and improve overall skin health.
Why EPA Is Essential for Brain Function?
The brain is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and EPA plays a crucial role in maintaining cognitive health and supporting optimal brain function throughout life.
1. Enhancing Neurotransmitter Function: EPA is involved in the production and regulation of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that facilitate communication between brain cells. By supporting healthy neurotransmitter function, EPA contributes to improved mood, cognitive performance, and overall mental well-being.
2. Protecting Against Age-Related Cognitive Decline: As we age, the risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases increases. EPA has neuroprotective properties that may help slow down age-related cognitive decline. It supports brain cell membrane fluidity, reduces oxidative stress, and helps maintain healthy blood flow to the brain, all of which are crucial for preserving cognitive function.
3. Supporting Mental Health: EPA has shown promise in supporting mental health, particularly in the context of mood disorders. Some studies suggest that EPA supplementation may help alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety. While more research is needed, the potential benefits of EPA for mental health are an exciting area of ongoing investigation.
4. Promoting Brain Development in Early Life: EPA is crucial for proper brain development during pregnancy and early childhood. Adequate intake of EPA during these critical periods supports the formation of neural connections and the overall structure of the developing brain. This early foundation can have lasting impacts on cognitive function and behavior throughout life.

Conclusion
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) is a powerful omega-3 fatty acid with wide-ranging benefits for heart health, inflammation reduction, and brain function. Its ability to support cardiovascular wellness, modulate inflammatory responses, and promote cognitive health makes it a valuable addition to a healthy lifestyle. While EPA can be obtained through diet, particularly by consuming fatty fish, many people choose to supplement with fish oil or algae-based EPA products to ensure adequate intake.
Incorporating EPA into your daily routine, whether through diet or supplementation, can be a proactive step towards better overall health. For more information on natural plant extracts and their potential health benefits, feel free to contact us at info@yanggebiotech.com. Our team of experts is here to help you make informed decisions about your health and wellness journey.
References
1. Calder, P. C. (2017). Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: from molecules to man. Biochemical Society Transactions, 45(5), 1105-1115.
2. Innes, J. K., & Calder, P. C. (2018). The Differential Effects of Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 532.
3. Dyall, S. C. (2015). Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: a review of the independent and shared effects of EPA, DPA and DHA. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 7, 52.
4. Mozaffarian, D., & Wu, J. H. (2011). Omega-3 fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: effects on risk factors, molecular pathways, and clinical events. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 58(20), 2047-2067.
5. Serhan, C. N., & Levy, B. D. (2018). Resolvins in inflammation: emergence of the pro-resolving superfamily of mediators. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 128(7), 2657-2669.
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- what is the difference between blue spirulina and pea powder?
- Unlock the Power of Albumin Peptide: A Revolutionary Step in Health and Wellness
- Beetroot Red: The Nutritional Powerhouse You Need
- Is Buying Spirulina Powder in China Safe?
- Amylase Enzyme Function
- Can Organic Psyllium Husk Powder Use in Baking
- Health Benefits of Seamoss Gummies
- Why Freeze-Dried Pitaya Powder is a Superfood You Need
- Activated Charcoal for Skin
- Top Benefits of Eicosapentaenoic Acid


