Creatine vs CaHMB: The ultimate showdown for muscle gain, who has the advantage?
On February 10, 2025, the National Health Commission approved the expansion of the dosage of CaHMB (β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate), a new food raw material, which is a great benefit to the application of CaHMB in the sports nutrition market.
CaHMB and creatine are both potential raw materials worth paying attention to in the sports nutrition market, creatine has achieved rapid growth in the global market in recent years, and CaHMB's favorable policies and new products are also continuing to launch, so what is the difference between creatine and CaHMB? What role will they "play" in the sports nutrition market?
CaHMB with creatine
What's The Difference?Creatine is a nitrogenous organic acid that is closely linked to muscle tissue and plays an important role in the body's energy supply, especially muscle and nerve cells. Creatine is mainly stored in skeletal muscle cells and plays a key role in maintaining muscle strength and promoting muscle recovery.
CaHMB, which stands for calcium β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate, is a calcium salt of β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid (HMB). β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid is found in a variety of foods and can effectively prevent muscle protein breakdown, and is also a minor metabolite of leucine in the human body, which can increase protein synthesis in skeletal muscle, reduce muscle damage and muscle breakdown after exercise, and contribute to normal exercise and muscle health.

Exploring the similarities
CaHMB is similar to creatine in that both are raw materials in the sports nutrition and health market, and both can be used in sports nutrition products. From the specific role point of view:
●Better athletic performance. Both CaHMB and creatine can help consumers have better athletic performance. CaHMB reduces muscle breakdown and promotes synthesis for strength and endurance. Creatine improves athletic performance by increasing intramuscular phosphocreatine stores.
● Supports muscle growth. Both ingredients are also able to support muscle growth.
●Reduces muscle damage. Both CaHMB and creatine are able to reduce muscle damage. Among them, creatine can help with muscle injury recovery after exercise; CaHMB can help people with impaired health to reduce muscle damage and loss, slow down protein metabolism, etc.

CaHMB has a large PK with creatine
There are also many differences between the two.
The mechanism of action is different
First of all, the mechanism of action of the two raw materials is different. As mentioned earlier: Creatine improves the ability of cells to resynthesize adenosine triphosphate by increasing intramuscular phosphocreatine stores, thereby supporting athletic strength, explosiveness, muscle mass, and more. CaHMB achieves its ability in various aspects of athletic performance by promoting muscle protein synthesis and slowing down muscle protein breakdown.

Suitable for different people
Although both ingredients can be used in the sports nutrition market, they are not suitable for the same people.
Creatine is suitable for people who "work out at high intensity" and is a very central part of the sports field. Such as professional athletes, sports enthusiasts, fitness bloggers, and so on. It is suitable for high-intensity, single/multiple short-term exercises, such as weightlifting, sprinting, etc., with more emphasis on (low-speed) strength, explosiveness, sprint performance and other sports. Creatine supplementation can support better athletic performance while reducing muscle damage, speeding up strength recovery, shortening recovery time for strenuous exercise, and more.
CaHMB is more suitable for the elderly, people in recovery, and people with more severe muscle health problems, or those who want to have more and better muscles. It can help older people cope with the natural deterioration of muscle mass and strength as they age.

Differences in the scope of application of regulations
CaHMB was approved as a new resource food as early as 2011, expanded in 2017, and expanded the approved consumption in February 2025, from the recommended dosage of 3g/day to ≤6g/day. The scope of application has not changed, and it is still used in beverages, milk and dairy products, cocoa products, chocolate and chocolate products, confectionery, baked goods, sports nutrition foods, and formulas for special medical purposes.
Creatine, according to the "National Food Safety Standard General Principles of Sports Nutrition Food GB 24154-2015", is an ingredient that must be added to speed and strength supplements in sports nutrition food in China, and is suitable for sprinting, high jump, ball, weightlifting, wrestling, judo, taekwondo, bodybuilding and strength equipment exercises. It cannot be used in health food or ordinary food, and the scope of application is relatively narrow compared to CaHMB. This has also led to the fact that in recent years, the growth rate of creatine in the international market has been very fast, while the domestic market has been tepid.
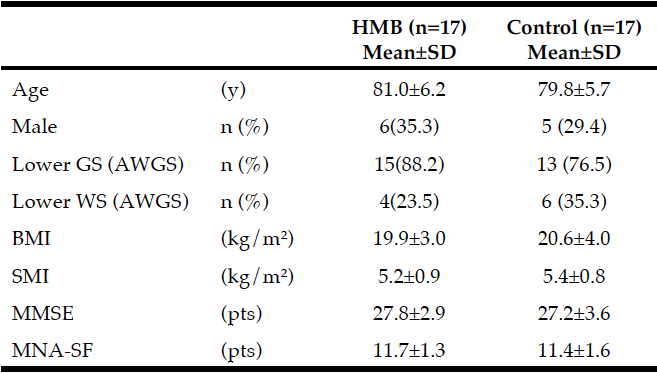
The richness of research in the field of scientific research varies
Although both raw materials have great potential, in fact, from the perspective of scientific research, there is a gap between the research richness of the two raw materials. According to the statistics of the search results of CNKI and PubMed, the number of research results of creatine is higher, at the level of tens of thousands; However, the research results of CaHMB are only at the level of hundreds or thousands, and the magnitude difference is more than 10 times.

Conclusion
On the whole, creatine and CaHMB are both potential raw materials for nutrition and health, and the two have similarities, but also have a certain degree of difference in scientific research, consumer cognition, terminal market, regulations, mechanism of action and suitable population.
Based on the domestic market, creatine has been clearly restricted by regulations, the growth is limited, and efforts need to be made in regulations to promote the application of creatine in the direction of health food and functional food.
CaHMB has great potential in this direction due to its distinctive characteristics in sports health, especially muscle health, and with the rapid growth of the sports nutrition market and the development of the silver economy, CaHMB will also usher in its growth opportunities.
For HMB and creatine, there’s no denying that they’re both a powerhouse. If you’re looking for bigger muscles, more strength, and power that is unmatched, you’ve found your guys.

